Configuring a JobLauncher
-
Java
-
XML
When you use @EnableBatchProcessing, a JobRegistry is provided for you.
This section describes how to configure your own.
The most basic implementation of the JobLauncher interface is the TaskExecutorJobLauncher.
Its only required dependency is a JobRepository (needed to obtain an execution).
-
Java
-
XML
The following example shows a TaskExecutorJobLauncher in Java:
...
@Bean
public JobLauncher jobLauncher() throws Exception {
TaskExecutorJobLauncher jobLauncher = new TaskExecutorJobLauncher();
jobLauncher.setJobRepository(jobRepository);
jobLauncher.afterPropertiesSet();
return jobLauncher;
}
...The following example shows a TaskExecutorJobLauncher in XML:
<bean id="jobLauncher"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.TaskExecutorJobLauncher">
<property name="jobRepository" ref="jobRepository" />
</bean>Once a JobExecution is obtained, it is passed to the
execute method of Job, ultimately returning the JobExecution to the caller, as
the following image shows:
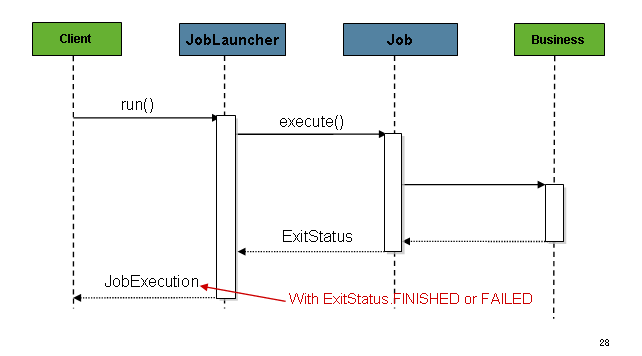
The sequence is straightforward and works well when launched from a scheduler. However,
issues arise when trying to launch from an HTTP request. In this scenario, the launching
needs to be done asynchronously so that the TaskExecutorJobLauncher returns immediately to its
caller. This is because it is not good practice to keep an HTTP request open for the
amount of time needed by long running processes (such as batch jobs). The following image shows
an example sequence:
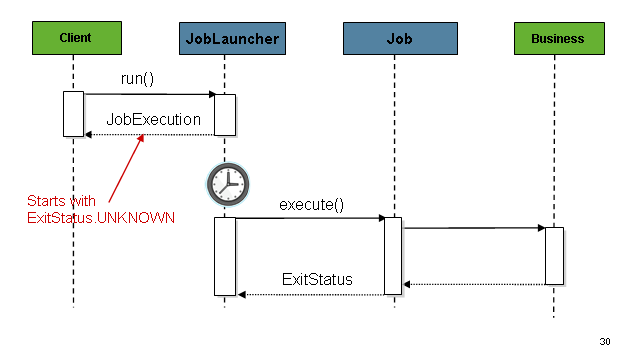
You can configure the TaskExecutorJobLauncher to allow for this scenario by configuring a
TaskExecutor.
-
Java
-
XML
The following Java example configures a TaskExecutorJobLauncher to return immediately:
@Bean
public JobLauncher jobLauncher() {
TaskExecutorJobLauncher jobLauncher = new TaskExecutorJobLauncher();
jobLauncher.setJobRepository(jobRepository());
jobLauncher.setTaskExecutor(new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
jobLauncher.afterPropertiesSet();
return jobLauncher;
}The following XML example configures a TaskExecutorJobLauncher to return immediately:
<bean id="jobLauncher"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.TaskExecutorJobLauncher">
<property name="jobRepository" ref="jobRepository" />
<property name="taskExecutor">
<bean class="org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor" />
</property>
</bean>You can use any implementation of the spring TaskExecutor
interface to control how jobs are asynchronously
executed.

